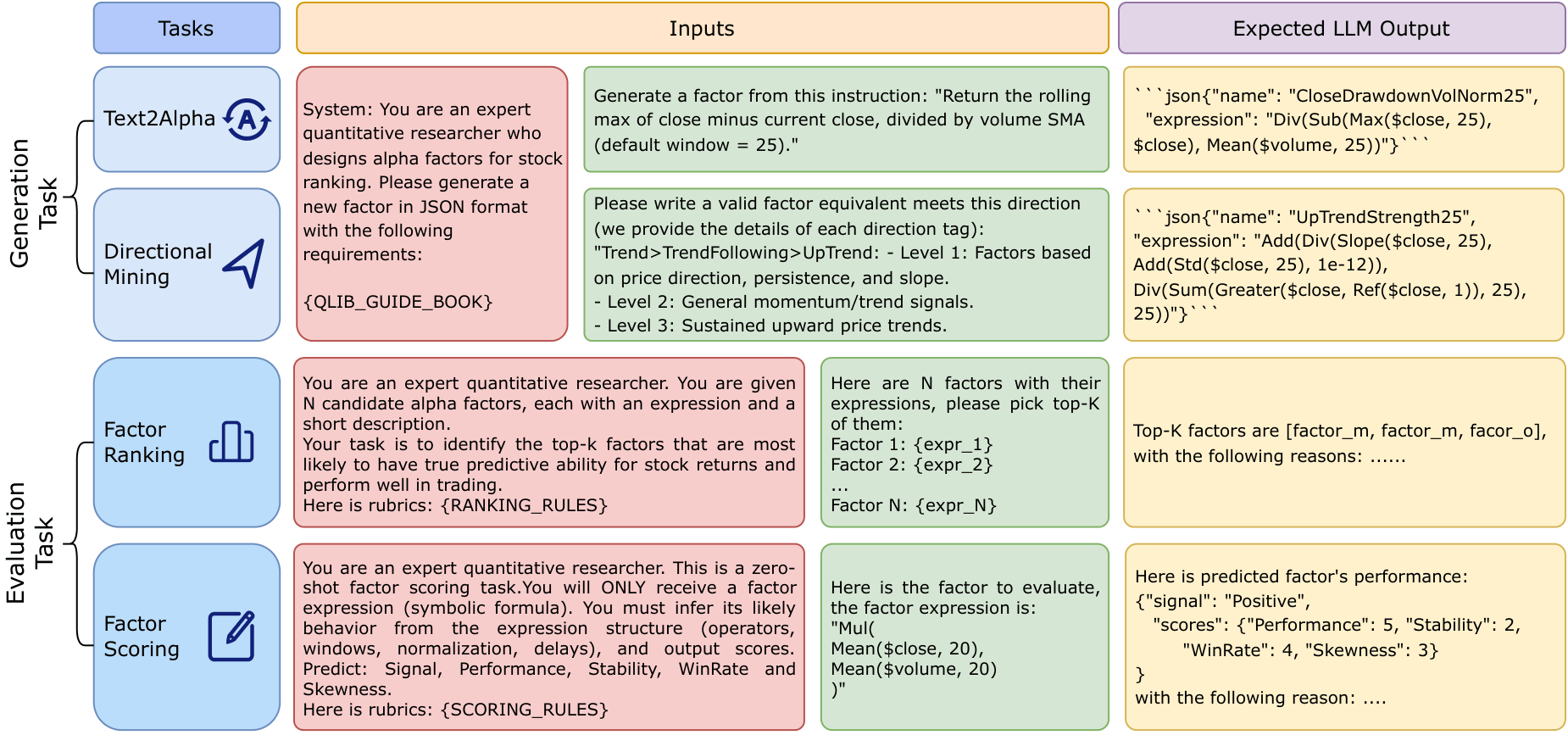
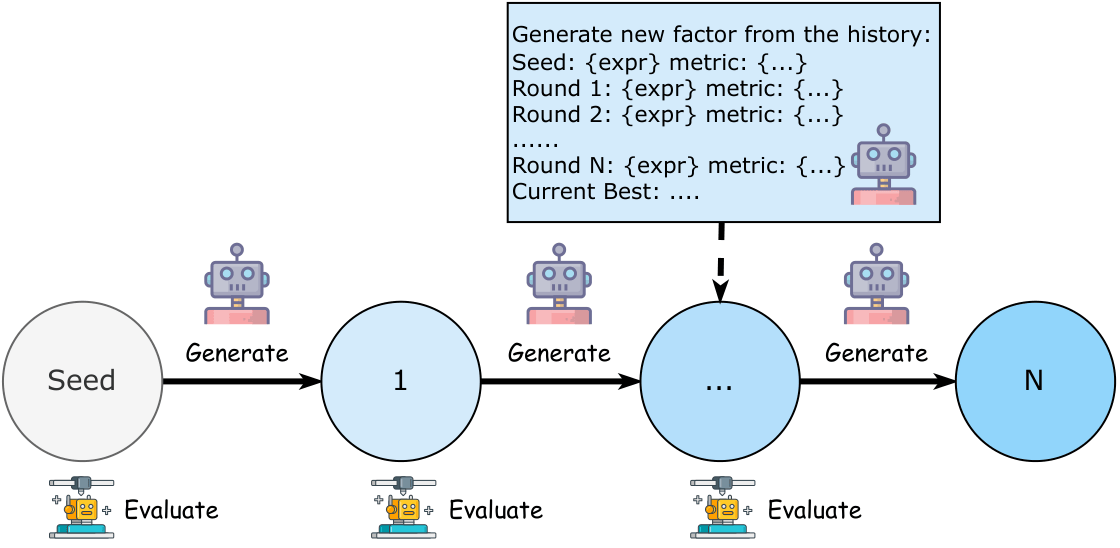
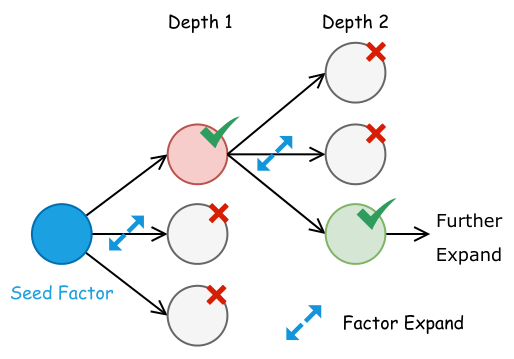
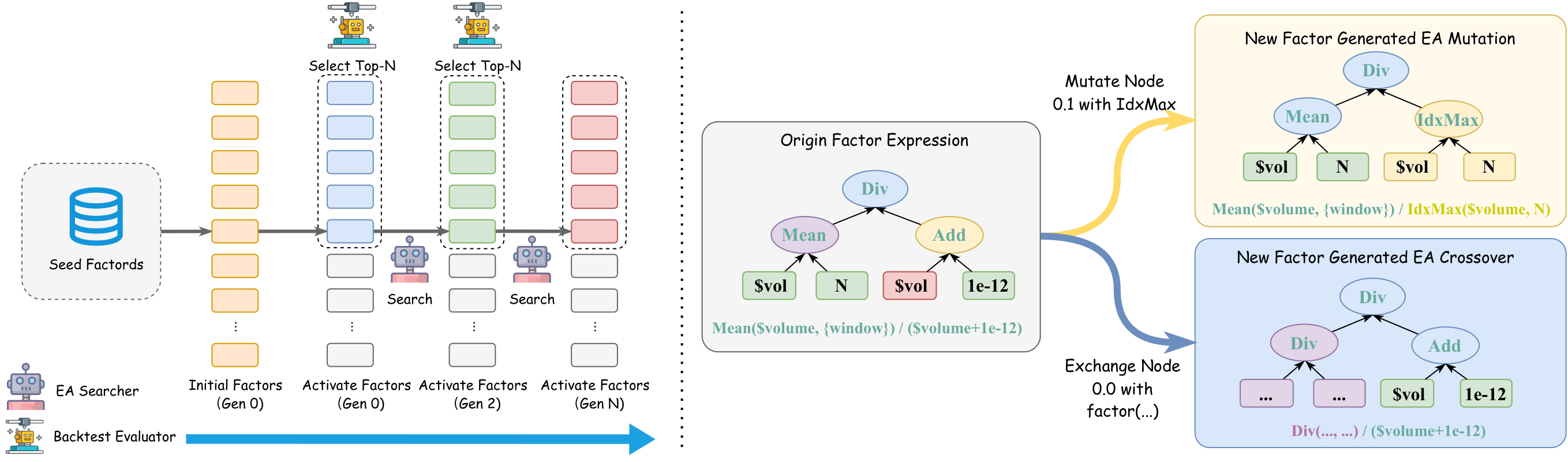
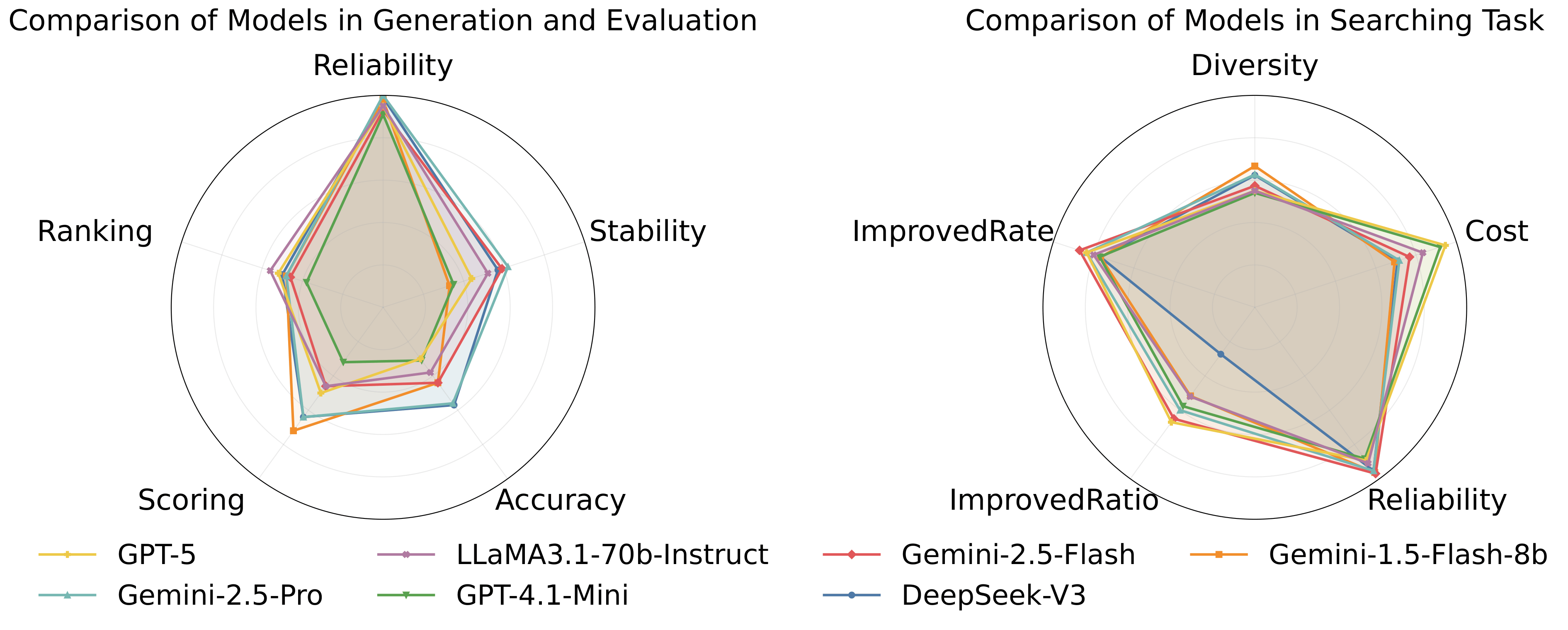
Overview
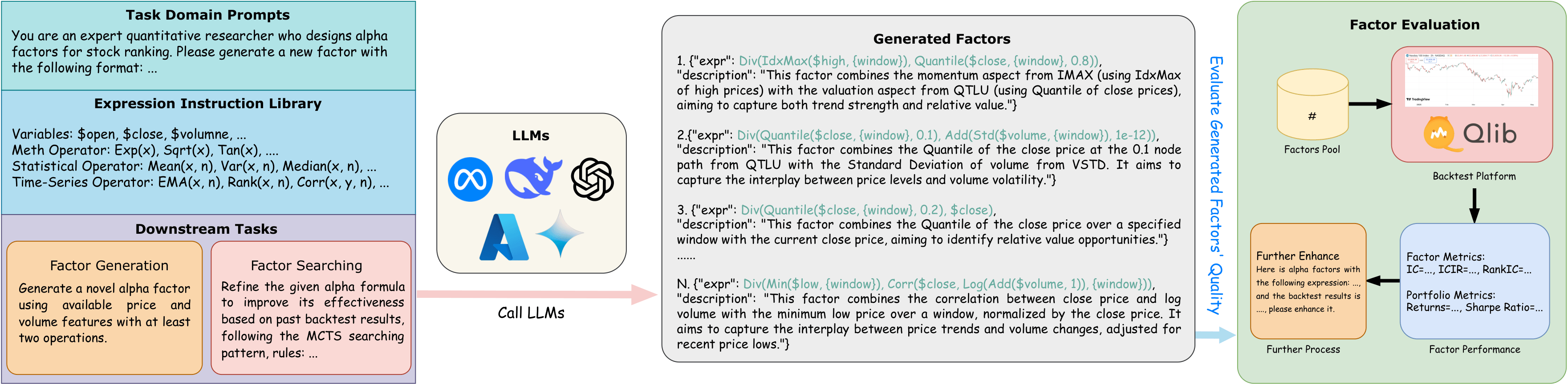
LLM-based Alpha Factor Mining Pipeline
This workflow illustrates how LLMs interact with prompts and backtesting engine (Qlib) to generate and refine formulaic alpha factors.
Core Problem
Recent works show that LLMs can generate alpha factors, but their true capabilities remain unclear:
- Can LLMs reliably generate valid, executable factor formulas?
- Can they evaluate factor quality without backtesting?
- Can they efficiently search the combinatorial factor space?
Our Solution
AlphaBench is the first systematic benchmark designed to evaluate LLMs across the entire formulaic alpha mining workflow, using:
- Executable factor expressions
- Real financial data
- Task-aligned quantitative metrics